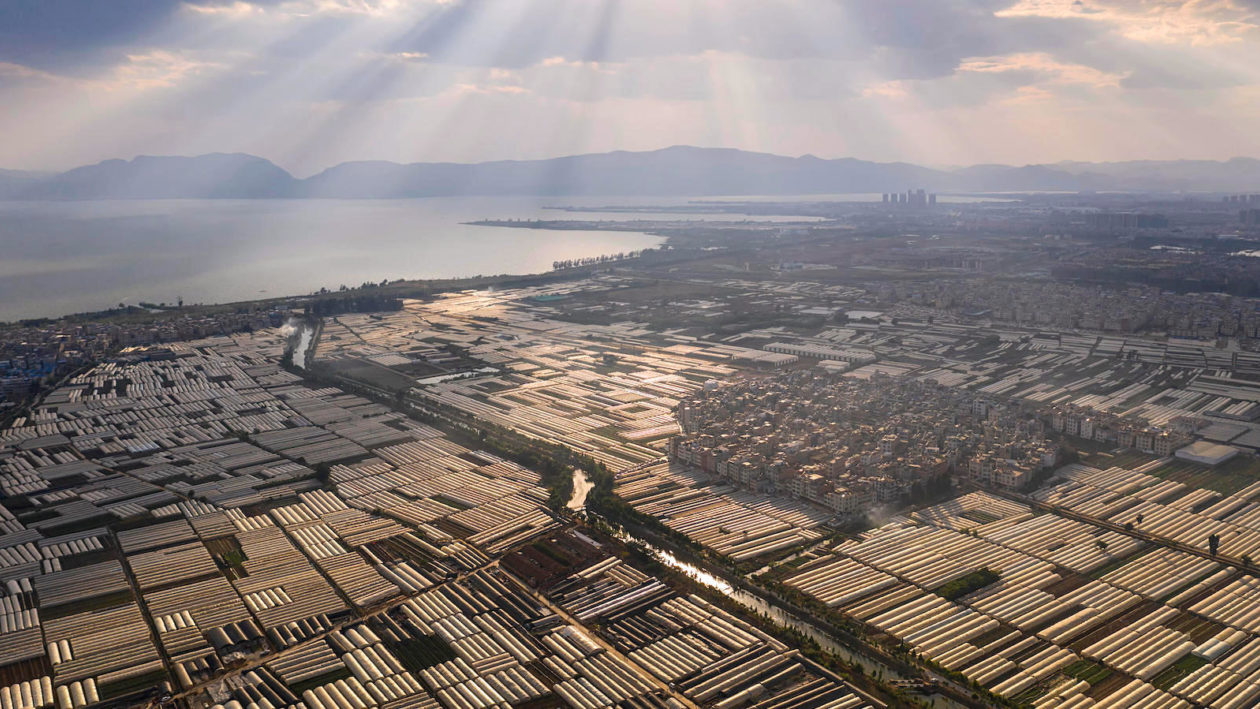
Skip the first half if you are short on time, but in the second half of this article you will find the fruition of imagination and courage we always hope to see more of:
The Unexpectedly Hopeful Paris Olympics
The Games have never lived up to all their ideals—some of which were dubious to begin with. And yet this year’s iteration, for all its flaws, has already inspired some positive change.
…Which brings me to the Seine. When the Olympics returned to Paris, in 1924, the swimming took place not in the Seine but in a pool, the Piscine des Tourelles. Swimming in the Seine was banned altogether one year prior. It was, after all, not merely a river but a road through Paris, crowded with barges. It was also a sewer, filled with refuse from houseboats and the untreated sewage that overflowed the city’s nineteenth-century system when it rained. Various attempts to clean up the Seine failed. When Paris was selected to host the 2024 Games, seven years ago, it was still illegal to swim in the river. Continue reading