Across a Continent, Trees Sync Their Fruiting to the Sun
European beech trees more than 1,500 kilometers apart all drop their fruit at the same time in a grand synchronization event now linked to the summer solstice.
Each summer, like clockwork, millions of beech trees throughout Europe sync up, tuning their reproductive physiology to one another. Within a matter of days, the trees produce all the seeds they’ll make for the year, then release their fruit onto the forest floor to create a new generation and feed the surrounding ecosystem.
It’s a reproductive spectacle known as masting that’s common to many tree species, but European beeches are unique in theirability to synchronize this behavior on a continental scale. From England to Sweden to Italy — across multiple seas, time zones and climates — somehow these trees “know” when to reproduce. But how?
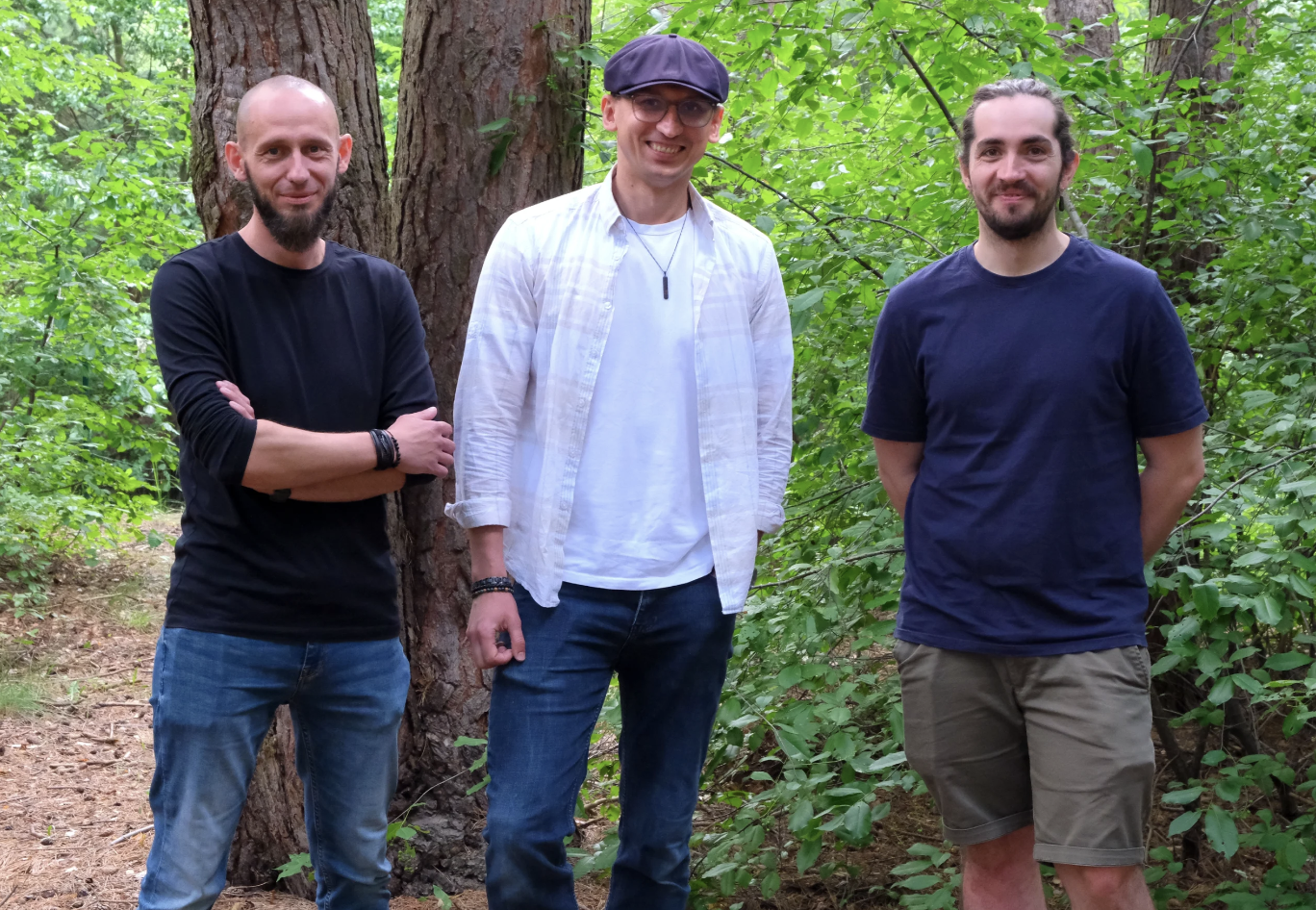

The recent discovery about European beech trees and the summer solstice was made by a team of researchers at Adam Mickiewicz University that included (from left to right) Jakub Szymkowiak, Michał Bogdziewicz and Valentin Journé, among others.
A group of ecologists has now identified the distinctive cue — what they call the “celestial starting gun” — that, along with balmy weather, triggers the phenomenon. Their analysis of over 60 years’ worth of seeding data suggests that European beech trees time their masting to the summer solstice and peak daylight.
Continue reading →