This spring, 160 chestnuts resulting from crosses made from large, standing American chestnut trees with natural blight resistance were planted at the botanic garden. Troy Thompson
Growing up in New England, apples and chestnuts were part of why autumn was my favorite season. During seven years living in walking distance of the Cornell orchards, apples remained a highlight of autumn well into adulthood. We have family who live in Boylston, so a visit to see this restoration project is now on my wish list. Thanks as always to Margaret Roach for all the gardens on that list:
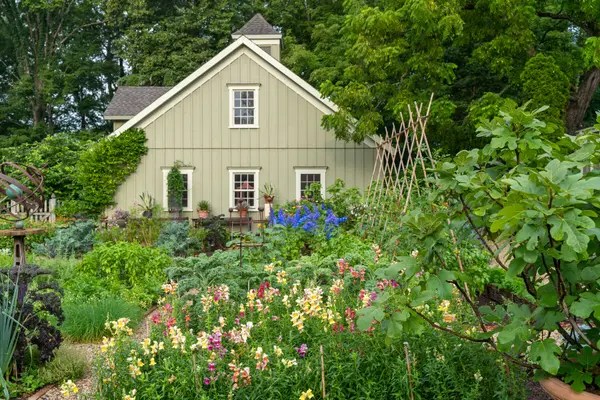
At the New England Botanic Garden at Tower Hill, in Boylston, Mass., the grafted heirloom apple trees are already big enough to bloom. But fruit isn’t expected for a few more years. New England Botanic Garden/Megan Stouffer
How Do You Restore a Chestnut Forest or an Apple Orchard? Very Slowly.
This botanic garden is determined to bring back the American chestnut tree and heirloom apples that taste like those grown 500 years ago. It won’t be easy.
“Explore what’s in bloom now,” exclaims a banner on the New England Botanic Garden at Tower Hill’s website. And, indeed, there is much to see. Continue reading