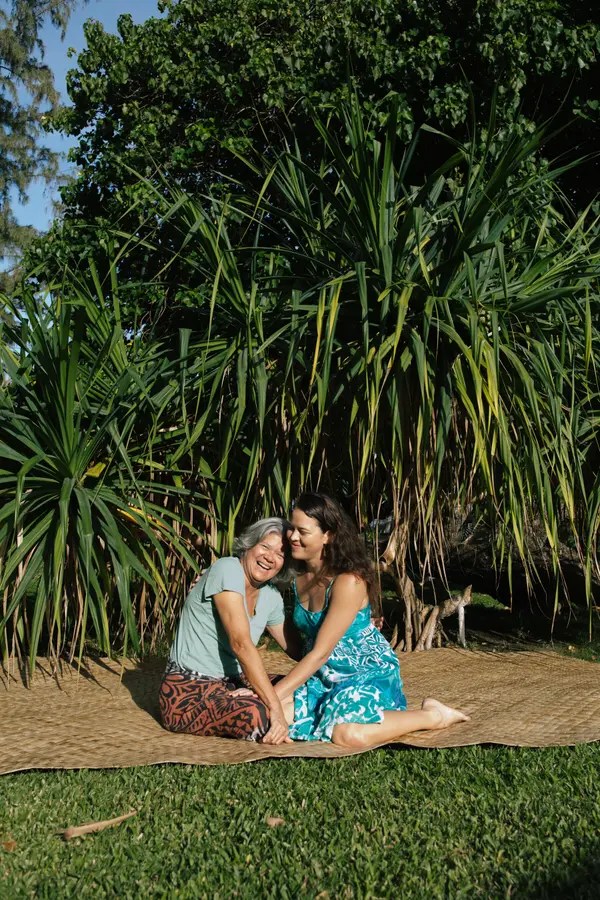
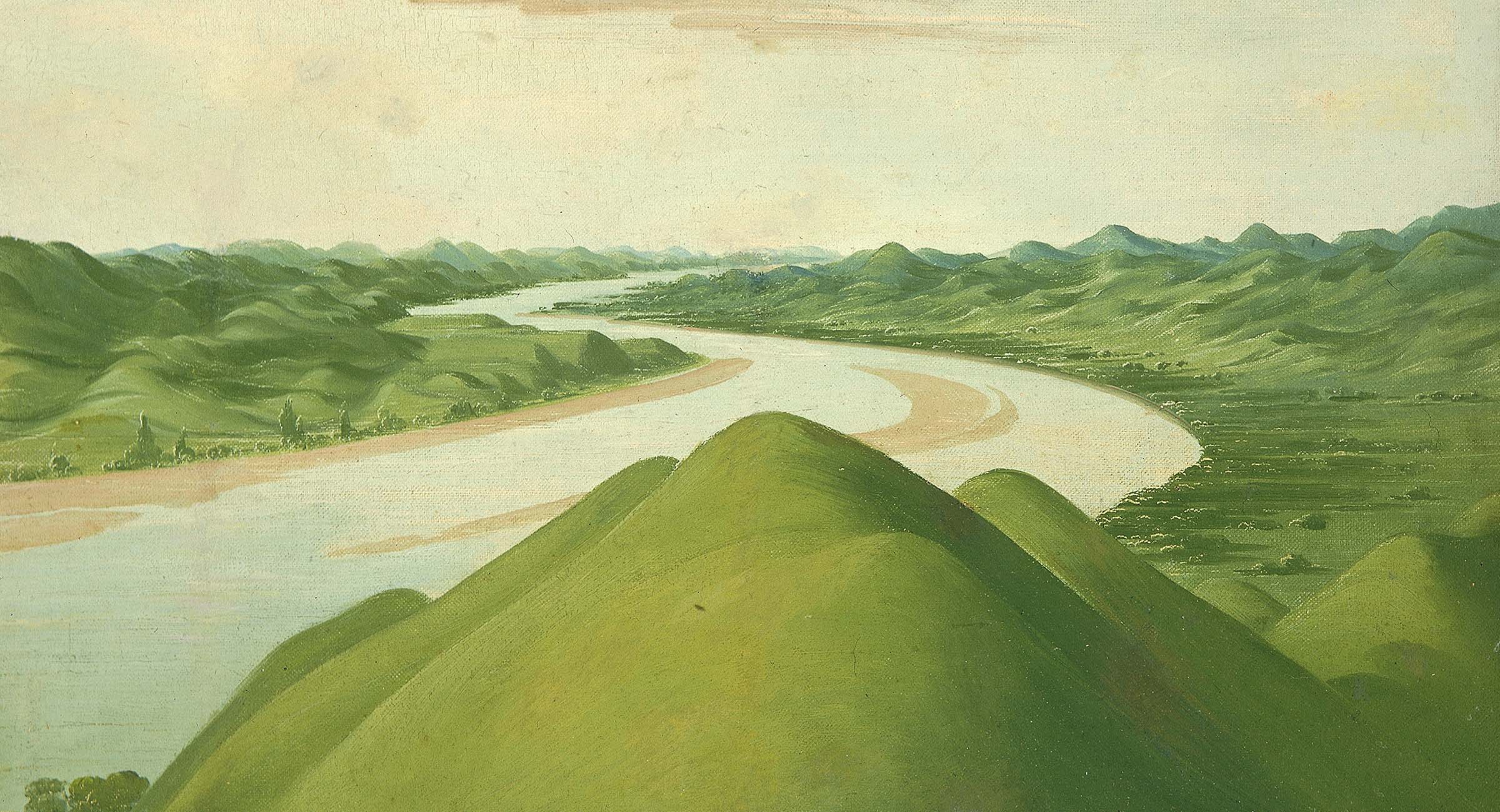
The Sycamore Gap tree, a beloved way marker, had grown for centuries along Hadrian’s Wall in England before vandals cut it down last year. Now little shoots have been discovered growing at its stump. Jason Lock/National Trust
When this act of vandalism was in the news last year, it felt terrible but had no meaning. But if the felled tree is giving new life, we must celebrate that:
Tiny Sprouts Spotted at the Stump of the Fallen Sycamore Gap Tree
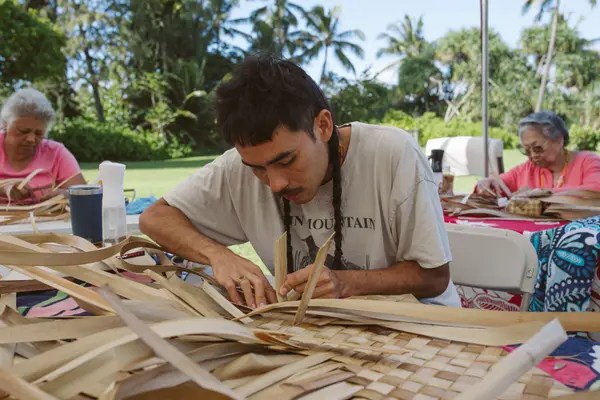
Gary Pickles, a ranger at Hadrian’s Wall Path National Trail, inspecting the Sycamore Gap tree shoots that recently appeared. Jason Lock/National Trust
Vandals last year chopped down the famed tree, which had stood on Hadrian’s Wall in England for nearly 200 years.
On a fine, bright morning last Friday, just like so many other fine, bright mornings, Gary Pickles took a walk.
Mr. Pickles, a ranger who works at Northumberland National Park in England, just south of the Scottish border, was inspecting a route that wends past Hadrian’s Wall, constructed by the Roman Army in the second century A.D. He walked past the cleft where the Sycamore Gap tree had famously jutted out into the landscape before it was illegally cut down last year, and he bent down to its stump. Continue reading